NPOL: GPM Precipitation Science Research Facility
Quasi-Vertical Profile
|
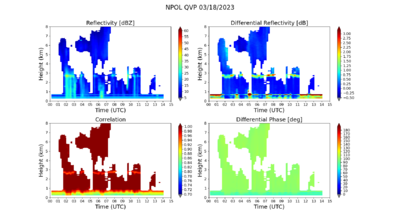
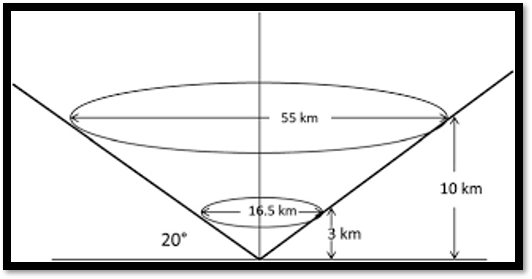
A quasi-vertical profile (QVP) is a conical scan at 20.0 degrees
elevation. The reflectivity, differential reflectivity, correlation,
and differential phase are azimuthally averaged by range bin, and are
presented in a height-versus-time format. A height of 10 km is
approximately 30 km range from NPOL (see figure). Per Ryzhkov et al.
2016, the temporal evolution of microphysical processes that govern
precipitation is a key benefit to this methodology. Through this
technique, NPOL will be monitoring characteristics and behavior of the
melting layer, regions of dendritic growth, riming, and snow aggregation
with high vertical resolution. Comparisons with vertically looking
remote sensors such as the Micro-Rain-Radar (MRR) and the GPM
Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) will be performed for
validation within the atmospheric column.
|
Click image to expand.
|
Previous QVP Plots
Grids
2020 Grid
2021 Grid
2022 Grid
Reference:
Ryzhkov A.V., P. Zhang, H. Reeves, M. Kumjian, T. Tschallener,
S. Tromel, and C. Simmer, 2016: Quasi-Vertical Profiles - A new way
to look at polarimetric radar data. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 33, 551-562.
|






